|
This page is under construction...
Understanding Photo Resolution & Picture Size
Photo Resolution:
Pixel = Picture Element 像素 = 相片元素
Pixel Aspect Ratio:
or rectangular
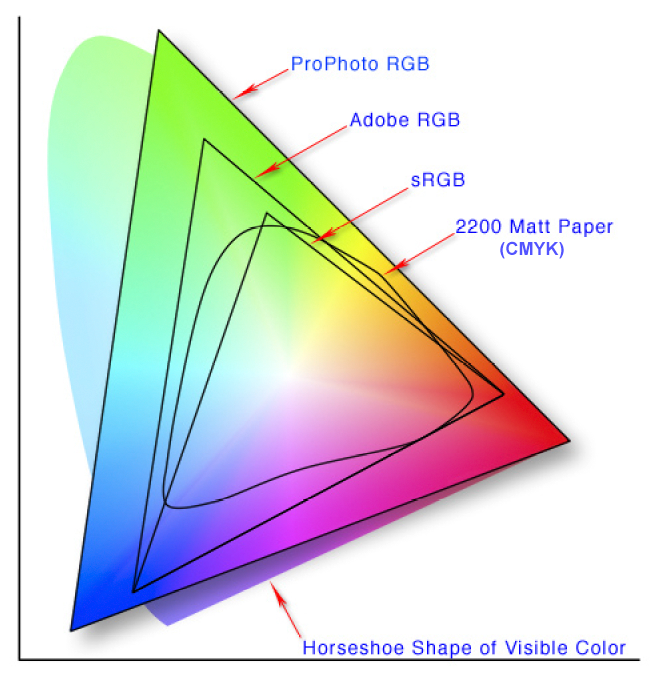
Color Space:
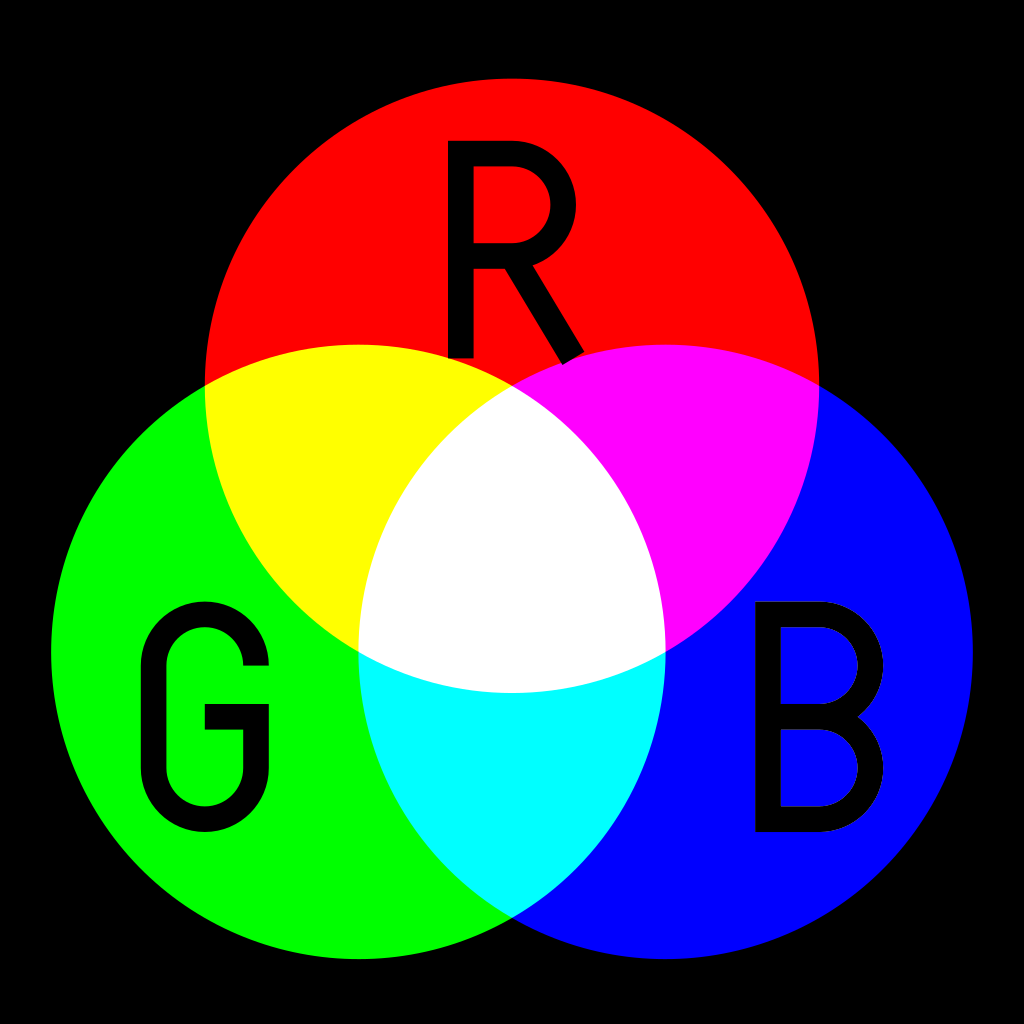
On screen display color: RGB = Red + Green + Blue
Additive color
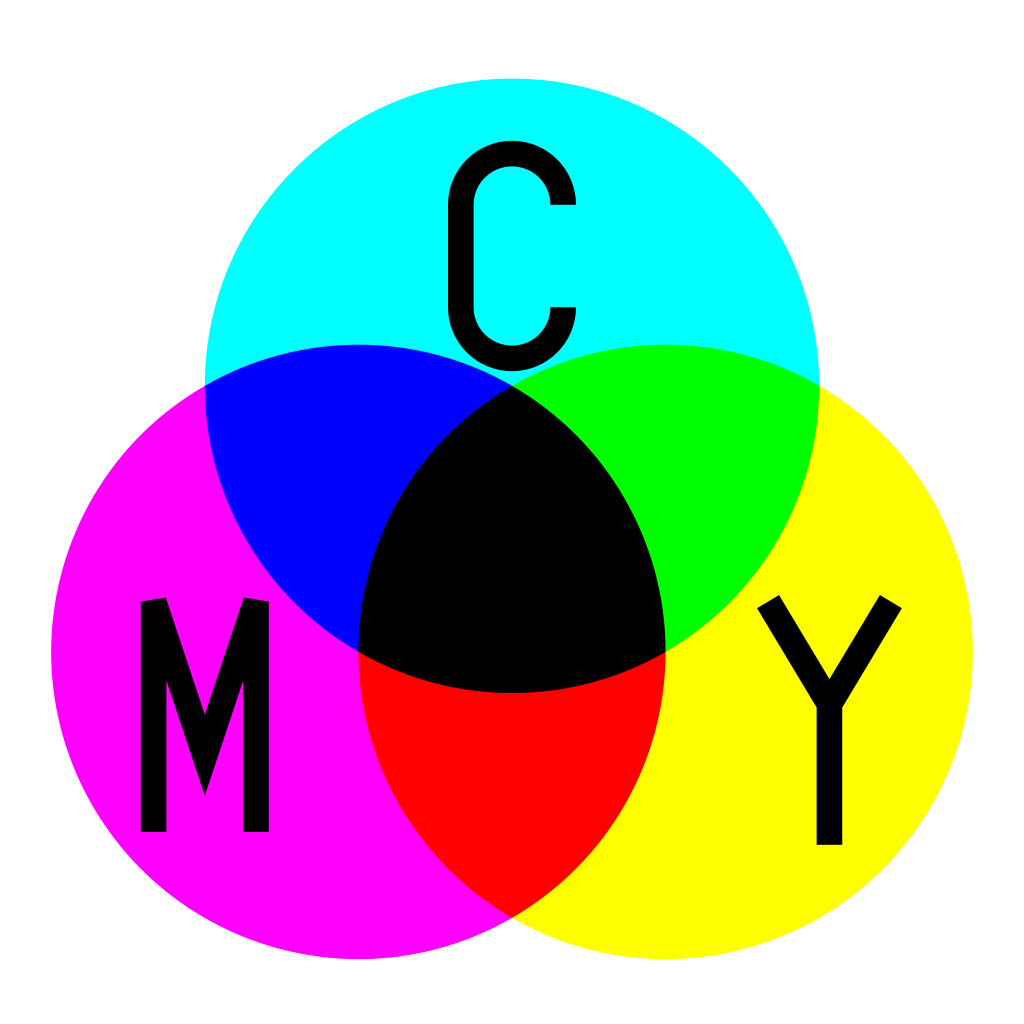
Printing Color: CMYK = Cyan + Magenta + Yellow + Black
Subtrative Color
Color comparison between RGB and CMYK:
Color depth is calculated by power of two ( 2n ), where n is the number of bit.
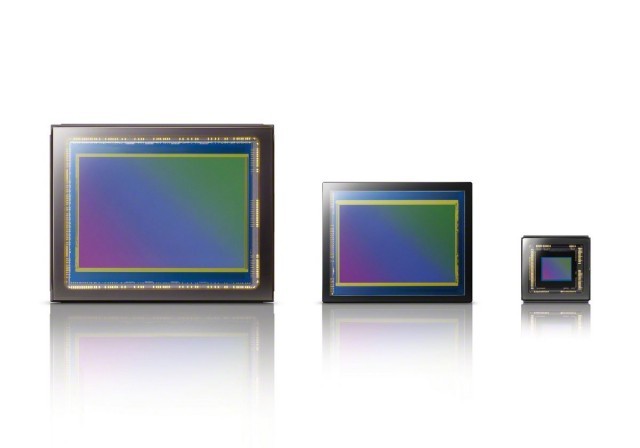
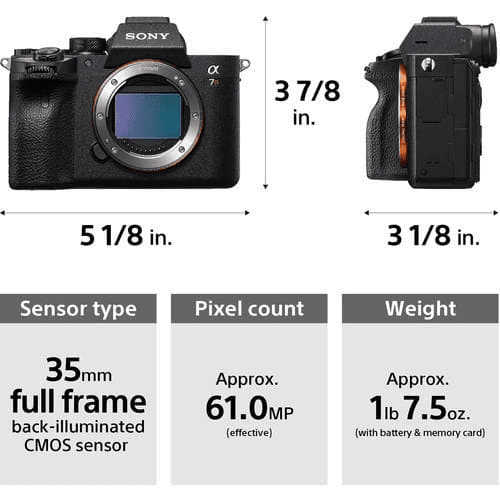
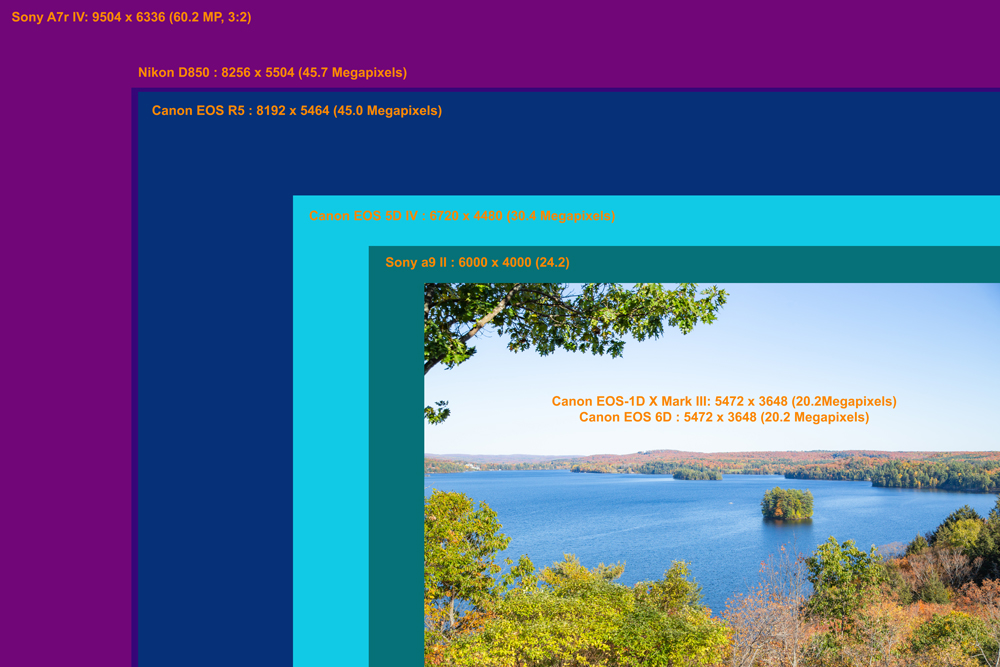
Camera Sensor to image:
Sony a9 II : 6000 x 4000 (24.2 Megapixels) Canon EOS-1D X Mark III: 5472 x 3648 (20.2 Megapixels) Canon EOS R5 : 8192 x 5464 (45.0 Megapixels) Canon EOS 5D IV : 6720 x 4480 (30.4 Megapixels) Canon EOS 6D : 5472 x 3648 (20.2 Megapixels) Nikon D850 : 8256 x 5504 (45.7 Megapixels)
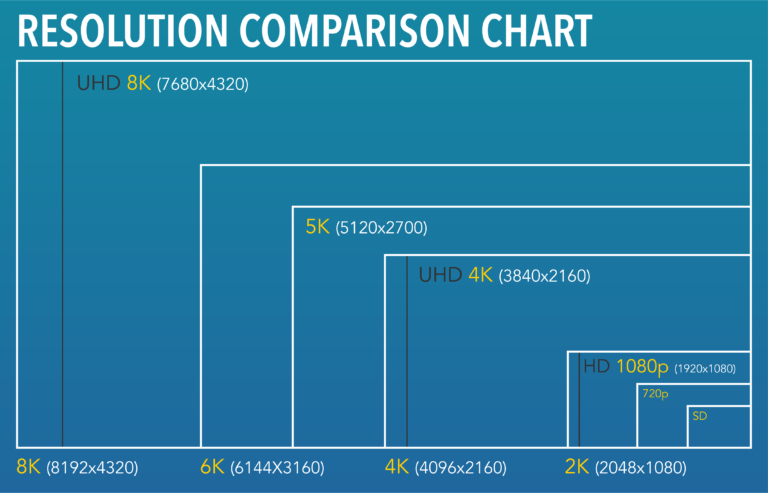
Standard Video Resolution:
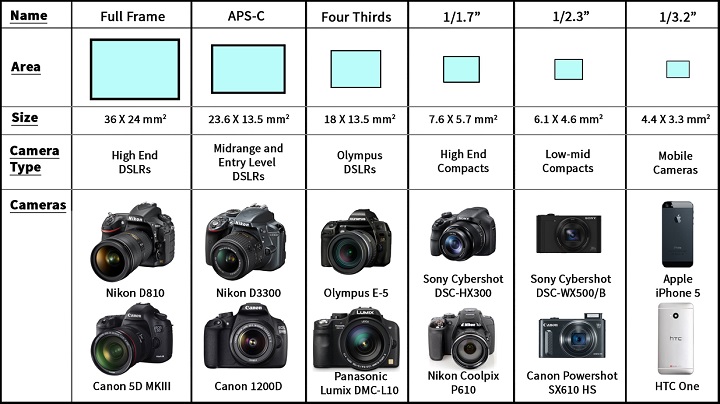
Sensor size:
Picture Size:
Display Size: Best image viewing quality in 1:1 or 100% viewing size.
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) or JPG is a commonly used method of lossy compression for digital images, particularly for those images produced by digital photography. The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality. JPEG typically achieves 10:1 compression with little perceptible loss in image quality.
Printing Size: DPI ( Dots Per Inch ) refers to the number of printed dots contained within one inch of an image printed by a printer.
300 dpi for art book, high quality magazine 150 dpi for newspaper 50 dpi for roadside poster
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) or TIF is a computer file format for storing raster graphics images, popular among graphic artists, the publishing industry, and photographers.
File Size: JPEG: Lossy format, small file size for screen display use. TIFF: Lossless format, larger file size for high quality printing use.
Summary: 1. JPG images are lossy in nature while TIFFs are lossless
|
||||||||||